
Until the past several years, common IT security philosophy focused on protecting the network perimeter and workstations to prevent cyber attacks. However, with organizations increasingly falling victim to attacks, it has become clear that protection requires new methods, based on Threat Intelligence.
Generating usable threat intelligence requires consistent dedication and high levels of expertise. The motivations of threat actors vary widely – from simple theft to identity theft to fraud. Every industry and organization has its own unique data to protect, a unique set of applications, and the technologies they use. All this brings tremendous variability in the ways attacks are executed, with new methods emerging every day.
Our Cyber Threat Intelligence team here at Hitachi Systems Security collects, analyzes, and assesses threats for our global client base. Our goal is to identify potential cyber threats and provide our clients intelligence and recommendations concerning how to manage and minimize these threats.
Essentially, our CTI group (Cyber Threat Intelligence) team tracks global trends, eCrime and hacktivist adversaries and deliver profiles of each actor to our client’s IT security team so they can understand attackers’ motivation and proactively defend against their tactics, capabilities, and tradecraft. We explain the why, what, and how of a potential attack, and discuss how threat intelligence will help thwart potential attacks. Hope you find the post helpful, interesting, and enjoyable!
Digital technologies lie at the heart of nearly every industry today. The automation and greater connectedness they afford have revolutionized the world’s economic and cultural institutions — but they’ve also brought risk in the form of cyberattacks. Threat intelligence is knowledge that allows you to prevent or mitigate those attacks. Rooted in data, threat intelligence provides context — like who is attacking you, what their motivation and capabilities are, and what indicators of compromise in your systems to look for — that helps you make informed decisions about your security.
“Threat intelligence is evidence-based knowledge, including context, mechanisms, indicators, implications, and action-oriented advice about an existing or emerging menace or hazard to assets. This intelligence can be used to inform decisions regarding the subject’s response to that menace or hazard.” — Gartner
Security operations teams are routinely unable to process the alerts they receive — threat intelligence integrates with the security solutions you already use, helping automatically prioritize and filter alerts and other threats. Vulnerability Management teams can more accurately prioritize the most important vulnerabilities with access to the external insights and context provided by threat intelligence. And fraud prevention, risk analysis, and other high-level security processes are enriched by the understanding of the current threat landscape that threat intelligence provides, including key insights on threat actors, their tactics, techniques, and procedures, and more from data sources across the web.

Today, the cybersecurity industry faces numerous challenges — increasingly persistent and devious threat actors, a daily flood of data full of extraneous information and false alarms across multiple, unconnected security systems, and a serious shortage of skilled professionals. Additionally, the attack surfaces IT organizations must manage and protect are larger now than ever before. Threats aren’t coming from one angle, organizations need to understand business risk from cyber-attacks, physical security and operational disruptions, attacks on their reputation, and more.
Some organizations try to incorporate threat data feeds into their network, but don’t know what to do with all that extra data, adding to the burden of analysts who may not have the tools to decide what to prioritize and what to ignore.
A threat intelligence solution can address each of these issues. The best solutions use a combination of machine learning to automate data collection and processing, integrate with your existing solutions, take in unstructured data from disparate sources, and then connect the dots by providing context on indicators of compromise (IoCs) and the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) of threat actors.
Threat intelligence is actionable — it’s timely, provides context, and can be understood by the people in charge of making decisions.
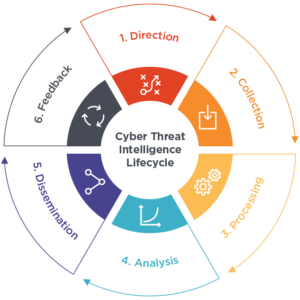
This stage involves planning out the goals, objectives, and methodology for the process of collecting threat intelligence based on the requirements of key stakeholders involved. During this stage security teams may set out to explore who the attackers are, their respective motivations, what the possible attack surface may look like and what measures need to be taken to improve defenses against a potential attack.
Establishing the goal of threat intelligence is also a crucial aspect of this stage i.e. who will benefit from the intelligence gathered - will it be executive management or a team of analysts? There is no point providing executive management a technical report when they would be better suited to receive a broader overview to inform their decisions.
Having established the requirements of the Threat Intelligence exercise in the planning stage, the team can then set out to collect the data required to satisfy the objectives defined in the first stage.
The raw data needed to address the requirements outlined in stage one can be sourced from a variety of both internal and external sources:
Once stage two is complete and raw data has been collected it then needs to be processed, this involves sorting and organizing it, which may include removing any false positives or redundancies. Essentially evaluating the data’s reliability and relevance before it can be analysed.
Even organizations with smaller digital footprints collect far too much data—hundreds of thousands of indicators on a daily basis—for humans to manually process, making automation particularly important to this time-consuming phase of the intelligence lifecycle.
After data has been processed, the team during this stage conducts a complete analysis of the data to arrive at answers to the questions created in the planning stage of the life cycle. The main objective of this stage is to convert processed data into the context required for the intended audience i.e. valuable recommendations and action items.
During this fifth stage the threat intelligence team presents their analysis in a report format fit for the intended audience outlined in the planning stage. For example, if the audience is executive management, then the threat intelligence needs to be in a format that can be easily consumed without security technical jargon and should be concise and to the point with cost effective recommendations/
While security teams tend to be most concerned with technical information such as malware findings and high-risk IP addresses, executive teams want to understand how cyber threats impact business risk, liability, and profit.
The final stage of the threat intelligence lifecycle involves getting feedback on the provided report to determine whether improvements need to be made for future threat intelligence activities. Stakeholders may have changes to their priorities or adjustments to how data should be disseminated or presented.
Periodic team surveys should be supplemented with an ongoing channel of communication via internal collaboration platforms. The goal is to constantly refine the intelligence gathering process, so that relevant and accurate information can be delivered to those who need it as quickly as possible.
Strategic threat intelligence provides a high-level view of the attack trends, techniques, and methods used by attackers, including their motivations and attributions and helps answer a specific set of questions:
Understanding these questions and mapping the answers to your critical assets, systems and business processes enables you to perform a thorough risk analysis, and communicate clear, relevant risk scenarios to your executive leadership team - and in doing so, justify investments in specific programs, technologies, and staff. Empowered by these insights, a company can focus its information security strategy on the areas pinpointed as cybercriminals’ prime targets and act quickly and with precision to repel intruders and minimize the risk of a successful attack.
Stay safe and thank you for taking the time to read our post.